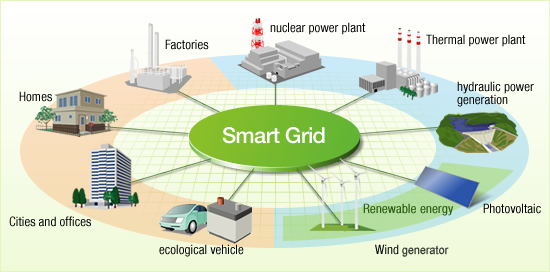
Smart Grid :
A smart grid is a modern electrical grid technology, which uses analog or digital information and communications technology to collect and act on information , related to suppliers and consumers automatically to improve the sustainability, efficiency, reliability and economics of the production and distribution of electricity.
The smart grid will make use of technologies like state estimation which will improve fault detection. Smart grid also allows self-healing of the network without involving any technician or electrician. This ensures better reliability in electricity supply and reduces any types of natural disasters.
Applications:
Smart grid technology is used in 5 key areas:
- Smart meters: Smart meters have already replaced analog meters with digital meters which shows reading in real time.
- Measurement and Sensing: The main reason for smart grid technology invention is evaluating congestion and grid stability and also monitoring health equipment, control strategies, support and energy theft prevention. Its applications also include electronic signature measurement , advanced switches and cables, digital protective relays and real time pricing tools.
- Phasor measurement units: Smart grid technology is used in high speed sensors called PMUs, which is distributed throughout a transmission network and can be used to monitor the state of the electric system. The rate of measurements taken by PMUs is up to 30 times per second,which is faster than the speed of existing technologies.

Electrical Grid:
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for delivering electricity from suppliers to consumers, which have generating stations that produce electrical power that is carried by high voltage transmission lines from distant sources to demand centers. These technologies allow distribution lines that connect individual customers.
Since power stations are located away from the population, the energy needs to be supplied a long way through, for which we need long transmission channels and make sure that power is not lost in the way. The transmission network will move the power to larger distances until it goes to the customer. So the main station first sends the energy to sub-stations , where it is stepped down transmission level to distribution level voltage. This technology to drive current to larger distance is Electric Grid technology. An emergency electrician could explain this much better than anyone.
Interconnections:
Grids in electric utilities are many times interconnected across the regions for improved economy and reliability. These Interconnections allow economic scale to purchase energy from large, efficient sources and also allows regions to have access to cheap bulk energy by receiving power from various sources.Utilities can take power from generator reserves from a different region in order to ensure continued reliable power and diversify their loads.
Applications:
- Its major application is the distribution of electricity to all the substations across international boundaries.
- The AC electrical grids consist of substations connected to each other by overhead, underground, and even a submarine line.
- It is implemented in Software parks, MS building, Stadium with flood lighting, street lighting, residential layout, industries and health/educational institutions.
Discussed above is a brief on Smart Grid and Electric grid.














